The Free Fall Trajectory of an Object Thrown Horizontally
Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory. An object moving horizontally may or may not be accelerated.

Quadratic Equation Applications Projectile Motion Scavenger Hunt Quadratics Quadratic Equation Projectile Motion
The object is called a projectile and its path is called its trajectoryAs an object travels through the air it encounters a frictional force that slows its motion called air resistance.

. Properties of Projectile Motion. N mg B Ff. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of building is shown as the dashed line in the figure.
When the center of mass of the block has been elevated by 300 m its velocity is 400 ms. Which of the following is true about the forces shown. A ball thrown horizontally has a constant sideways velocity apart from a slight loss of momentum due to air resistance.
If additionally α 90 then its the case of free fall. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. What is the horizontal distance covered by the particle.
It is the horizontal distance covered by projectile during the time of flight. One end of a string is attached to the ball so that it is spun in a horizontal circle of radius R at tangential speed vo as shown in Figure 1 above. The free body diagram is shown below.
It is equal to OA R O A R. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. Asked May 21 2019 in Kinematics by Nakul 70.
A a ball that was thrown horizontally b a ball that was thrown at an angle above horizontal c a ball that was thrown at an angle below horizontal d a ball that was dropped e all of the above 7. After the initial force that launches the object it only experiences the force of gravity. Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory.
If the vertical velocity component is equal to 0 then its the case of horizontal projectile motion. Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown projected into the air. T2pi sqrt r3GM A ball of mass M is on a horizontal surface with negligible friction.
The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. A baseball player is trying to determine her maximum throwing distance.
The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. Free fall Activity 1 1. Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory.
Upon reaching the peak the projectile falls with a motion that is symmetrical to its path upwards to the peak. Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory. The vertical velocity component Vy is equal to V sin α.
A 500 kg block with an initial velocity of 100 ms is projected up a rough 30 incline. So R Horizontal velocity Time of flight u T u 2h g R Horizontal velocity Time of flight u T u 2 h g So R u 2h g R. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure.
Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory. Free fall is always uniformly accelerated. N mg 7 F mg The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of.
Which sets of arrows best corresponds to the directions of the velocity and acceleration for the object at the point P on the trajectory. N mg E Ff. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure.
Range horizontal distance travelled by the projectile Height maximum vertical distance reached by the projectile. If an object is thrown horizontally with an initial speed 10 ms-1 from the top of a building of height 100 m. With an initial velocity of 150 ms an object moving along a horizontal surface is acted upon by the two forces shown below.
A projectile is launched at an angle to the horizontal and rises upwards to a peak while moving horizontally. A body in free fall moves with a constant acceleration. However a body projected horizontally may or may not move with a constant acceleration.
Which of the following objects are in free fall. Trajectory path travelled by the projectile. Velocity acceleration A B C D E 10.
She must release the. N mg C Ff. Three vectors - V Vx and Vy - form a right triangle.
Free fall is always accelerated motion. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. A free-body diagram for the ball at an instant in time is shown in Figure 2.
The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. The free fall trajectory of an object thrown horizontally from the top of a building is shown as the dashed line in the figure. Which sets of arrows best correspond to the directions of the velocity and of the acceleration for the object at the point labeled P on the trajectory.
It may only have a uniform velocity or may be accelerating. N mg D F f. Answer 1 of 3.
A ball that is released at the same height with no sideways velocity accelerates downwards at G 981 m.
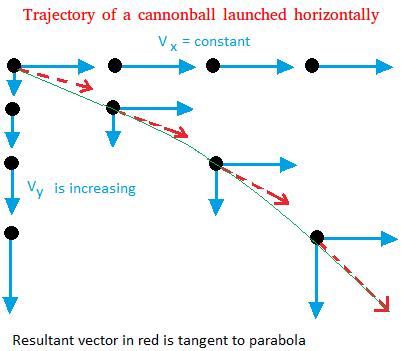
Projectile Launched Horizontally
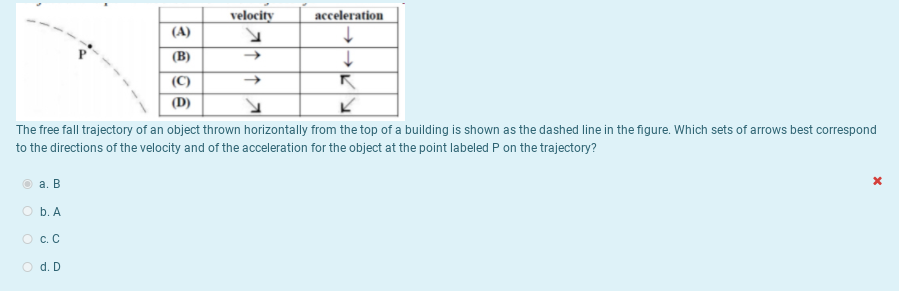
Answered The Free Fall Trajectory Of An Object Bartleby

How To Solve Projectile Motion Problems Applying Newton S Equations Of Motion To Ballistics Projectile Motion Math Projects Quadratics
The Free Fall Trajectory Of An Object Thrown Horizontally From The Top Of A Building Is Shown As The Dashed Line In The Figure Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Comments
Post a Comment